Recipes
Some healthy mediterranean recipes from Prof. Dr. Berrino
Recommended intake of nutrients
On the official website of the Swiss Nutrition Society (SGE-SSN) you will find all the nutritional recommendations, i.e. the recommended intake of a certain nutrient, depending on the age. These recommendations have been summarized in practical tables in DE, FR and IT.
Copyright © SGE-SSN, only for information.
Why my posts on nutrition?
Don’t rely on supplements
One of the Cancer Prevention Recommendations is to aim to meet nutritional needs through diet alone.
The Panel recognizes that dietary supplements, in addition to varied diets, may at times be beneficial for specific population groups:
-vitamin B12 for people over the age of 50 who have difficulty absorbing naturally occurring vitamin B12
-iron and folic acid supplements for women who may become or are pregnant
-vitamin D supplements for infants and young children and for pregnant and breastfeeding women, although specific recommendations for iron and vitamin D supplementation vary between countries
In crisis situations it is necessary to supply supplements of nutrients to such populations or to fortify food to ensure at least minimum adequacy of nutritional status. For more read the WCRF website:
https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/recommendations/dont-rely-supplements
© Copyright World Cancer Research Fund (WCRF), 2018.
All Rights Reserved.
Only for information after permission of the WCRF.
Proteins
Food proteins are present in animal and vegetable foods.
The daily intake is 0,8 % of the body weight.
For example: 43 g of proteins for a 54 kg body weight.
In proteins there are different amino acids, some of which are essentials. This means that our body is unable to synthesise them by itself and must take them through food.
The biological value (quality) of the protein is given by the quantity of essential amino acids inside the protein.
For more information refer to this link of our Swiss Authorities (DE, FR, IT). In this link under “further information”, you can find a document (pdf) containing more information on protein in different languages (here the link of the document: DE, FR, IT).
Examples of proteins are casein (milk protein) or gluten (wheat protein), but proteins compose a huge of biochemicals (like hormones, enzyme and so on). You can find a high quantity of proteins in fish, legumes, soy (tofu), quorn and seitan.
Vitamin D
Functions of vitamin D in the Body
Building and maintaining bones and teeth
Controlling cell division
Strengthening the immune system
Maintaining normal muscle function
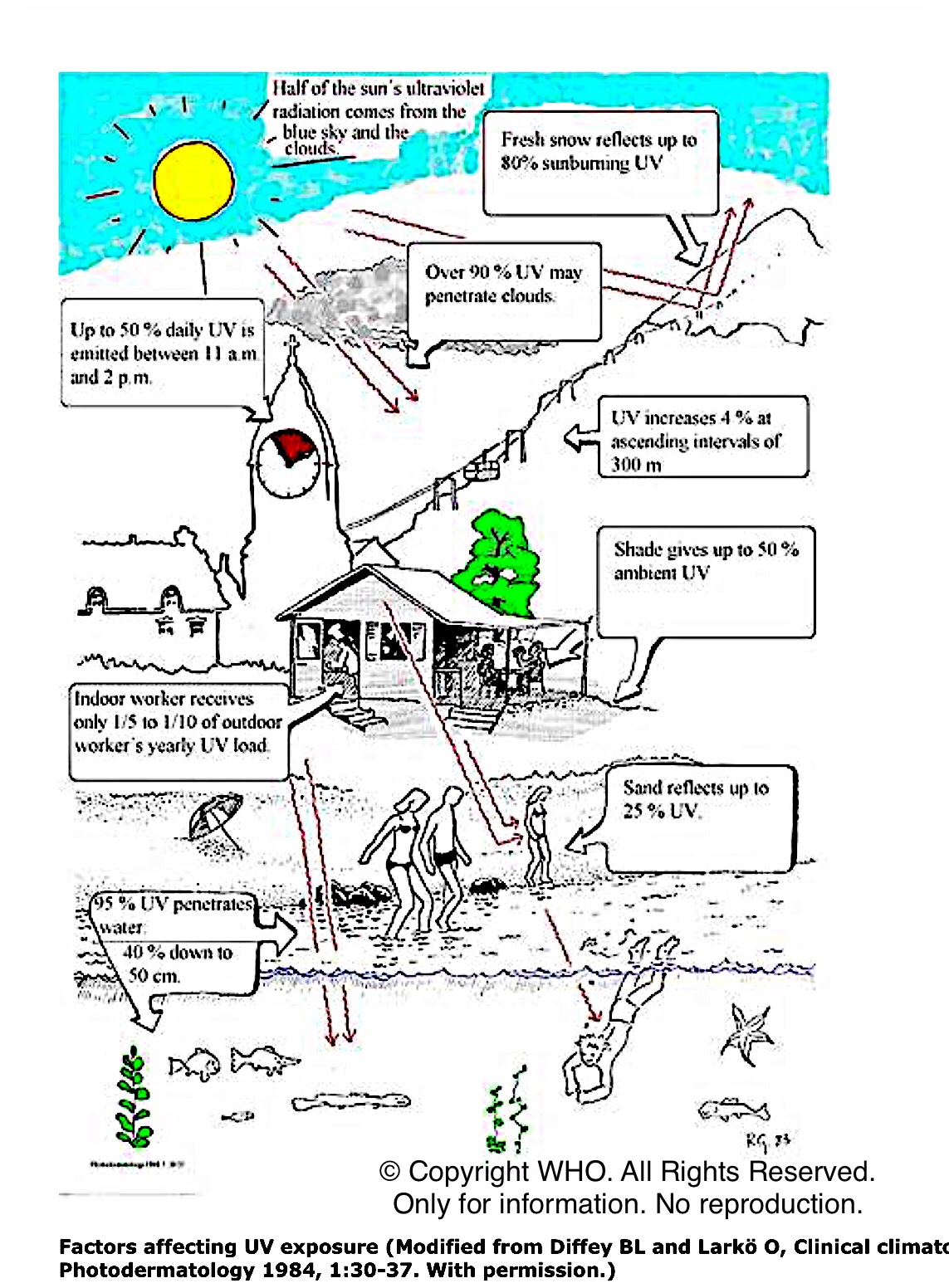
Vitamin D content is too low in foods (only in small quantities) to meet the adult body’s daily requirement (ca. 15-20 µg/600-800 IU), depending on age and for pregnancy. The food containing this small quantity are mushrooms, seafoods, green vegetables, eggs. Vitamin D (cholecalciferol / vitamin D3) is the only vitamin that the body produces itself, with the help of UVB (biologically damaging rays, most absorbed by the atmosphere, ozone) and sunlight. UV exposure is not a good idea, due to the harmful effects of UV rays. So please follow these recommendations for sun exposure:
1.avoid bright sunshine (e.g. 11:00 – 15:00)
2.protect your skin with a sunscreen
3.protect your eyes with sunglasses
In summer the body’s vitamin D production is usually sufficient. However, when there is a deficiency or an increased need, vitamin D can be taken in the form of drops, based on consultation with a physician.
The scientific sources of this text are:
the Swiss Cancer League (DE, FR, IT, EN) in Vitamin D
the World Health Organization (WHO) in http://www.who.int/uv/publications/proUVrad.pdf
For more (EN, FR, other languages) on http://www.who.int/uv/fr/
For more information, visit the Swiss Authorities link in different languages (DE, FR, IT). Please choose your language at the top of the website.
At the bottom of this website under “further information” , you can find 3 documents as pdf, explaining all about vitamin D (Q&A, scientific information, recommendations). I invite you to read them, the informations are up-to-dated and reliable (here the link of the document: DE, FR, IT: raccomandazioni-vitamina-d)
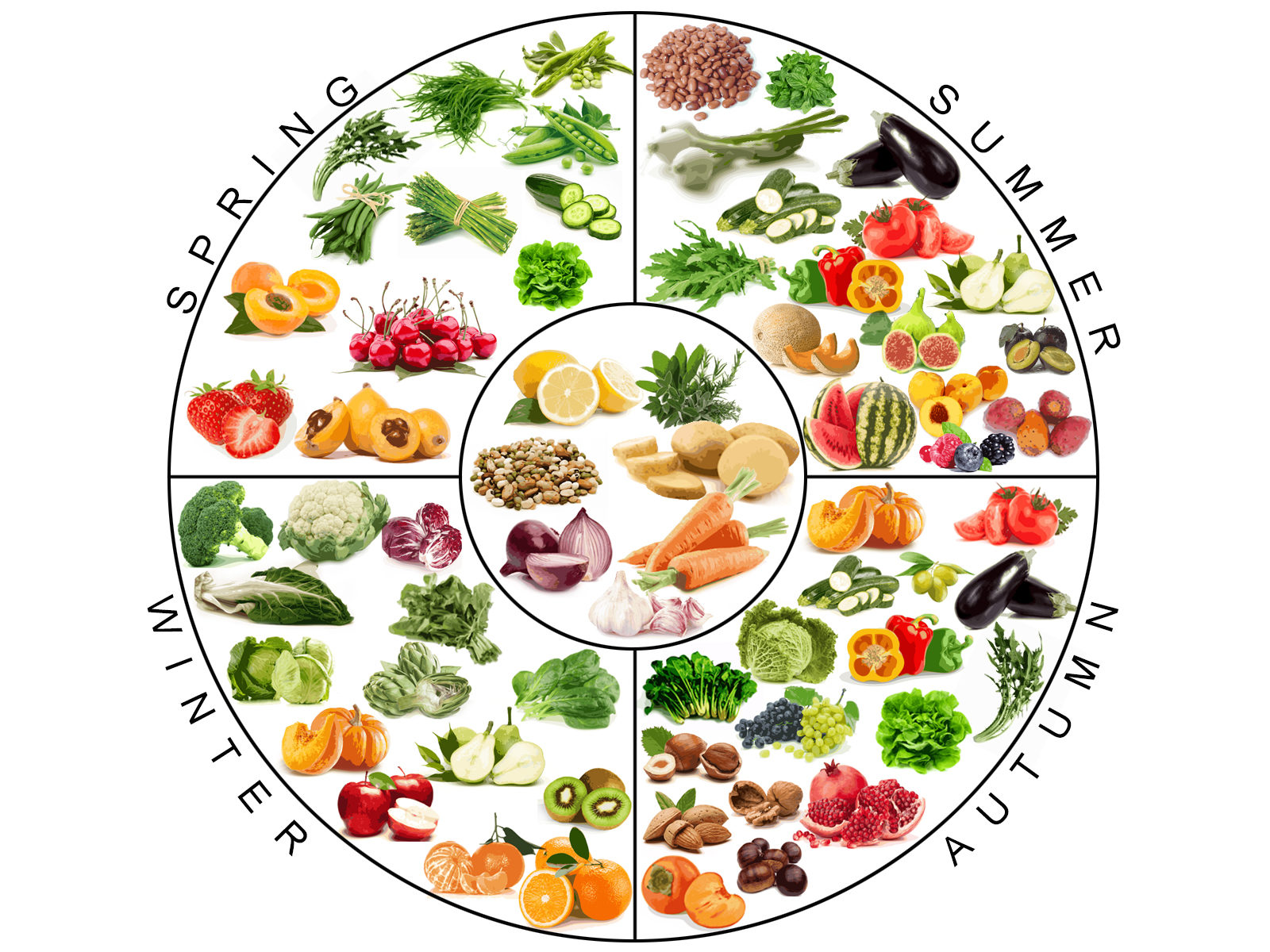
Seasonality of fruit and vegetable
In this article, you can find the seasonality of fruit and vegetable (tables are in IT, DE, FR). Please notice that the seasonality described here refers to the Mediterranean basin and should be taken as a general indication (here for Switzerland).
Please consider also the meteorological differences occurring during the year and, prefer local and organic (BIO) fruit and vegetable
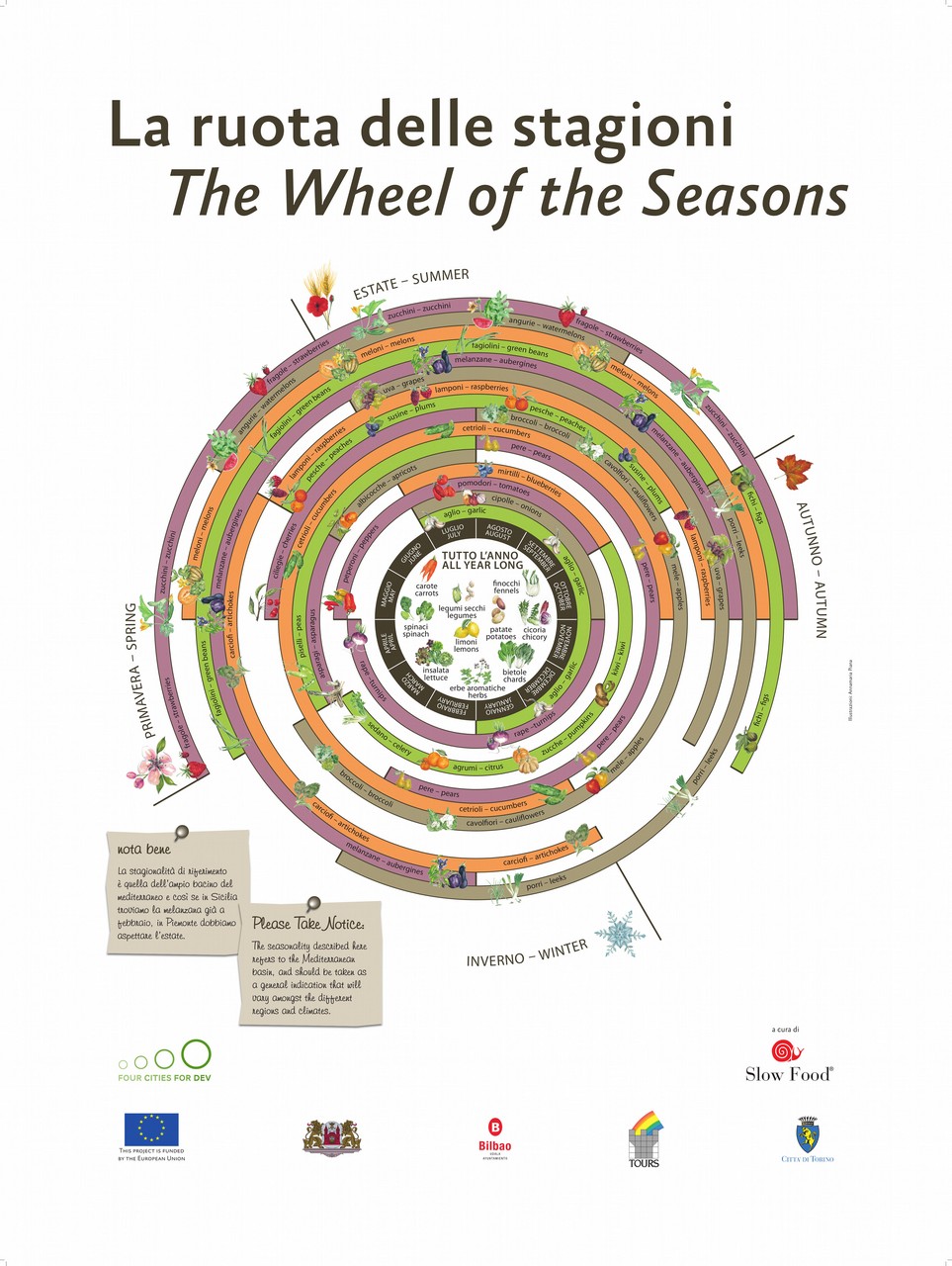
The tables below have been officially drafted by the FOAG (Federal Office for Agriculture, in German: Bundesamt für Landwirtschaft – BLW, in French: Office fédéral de l’agriculture – OFAG, in Italian: Ufficio federale dell’agricoltura -UFAG).
Please visit the official links below to open directly the seasonality table as a pdf document of 2 pages, drafted pro each language (German – DE, French – FR, Italian – IT).
How can I eat correctly?
I invite people to restore value to the food road, eating only local, seasonal and organic foods which consists of:
– whole grains (25% of the meal)
– protein-rich foods, like pulses (25% of the meal,, max 6% protein)
– vegetables (3 portion of 120g or 50% of the meal)
– fruits (1-2 portions of 120g, eat on the morning and not after 2 pm)
Substituting step-by-step added sugars with fruit and overly salted foods with foods with low salt. If needed: adding 2-3 portions of seafood per week or 1 egg each 2 weeks.
What fish can I eat?
Fish delivers an impressive dose of omega-3 fatty acids that our bodies need to grow and thrive, and vitamin B12, in addition to other substances.
Prefer small seafood at the bottom of the food chain—for example, anchovies, sardines, and herring—are more plentiful than their larger cousins, grow more quickly, and contain fewer contaminants, making them sustainable and healthy choices.
We might prefer small blue fish, which contains an amount of selenium (one of the properties of selenium is to counteract mercury contaminant, binding it to an inactive compound). A list of small blue fish could be easily found on internet, in your language.
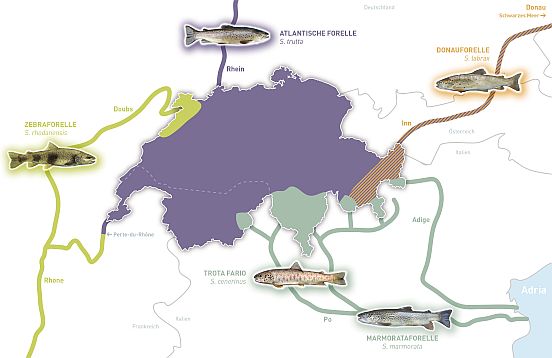
A wonderful local trout (rich on vitamin B12 more then all other food, see my post on it) fished in a small alpine lake like in Engadin is the best choice for our health.
Try to avoid the varieties, which may suffer from overfishing, heavy mercury load, and/or other problems: Chilean sea bass, Atlantic cod, grouper, imported king crab, king mackerel, orange roughy, Atlantic salmon, imported shrimp, swordfish, and Atlantic Bluefin tuna.
Prefer seafood fished at sea or lake or river (only in clean waters) but not farmed. Farmed fish often feast on pesticides, antibiotics or other substances.
To be up-to-date with the clean waters of our ocean/sea consult for example this link below (select clean waters score for the country you want to know about): http://www.oceanhealthindex.org
The image of the trout is taken from this website, Swiss Fisheries Consulting Office ( in DE, FR, IT): https://www.fischereiberatung.ch/index









