Functions of vitamin D in the Body
Building and maintaining bones and teeth
Controlling cell division
Strengthening the immune system
Maintaining normal muscle function
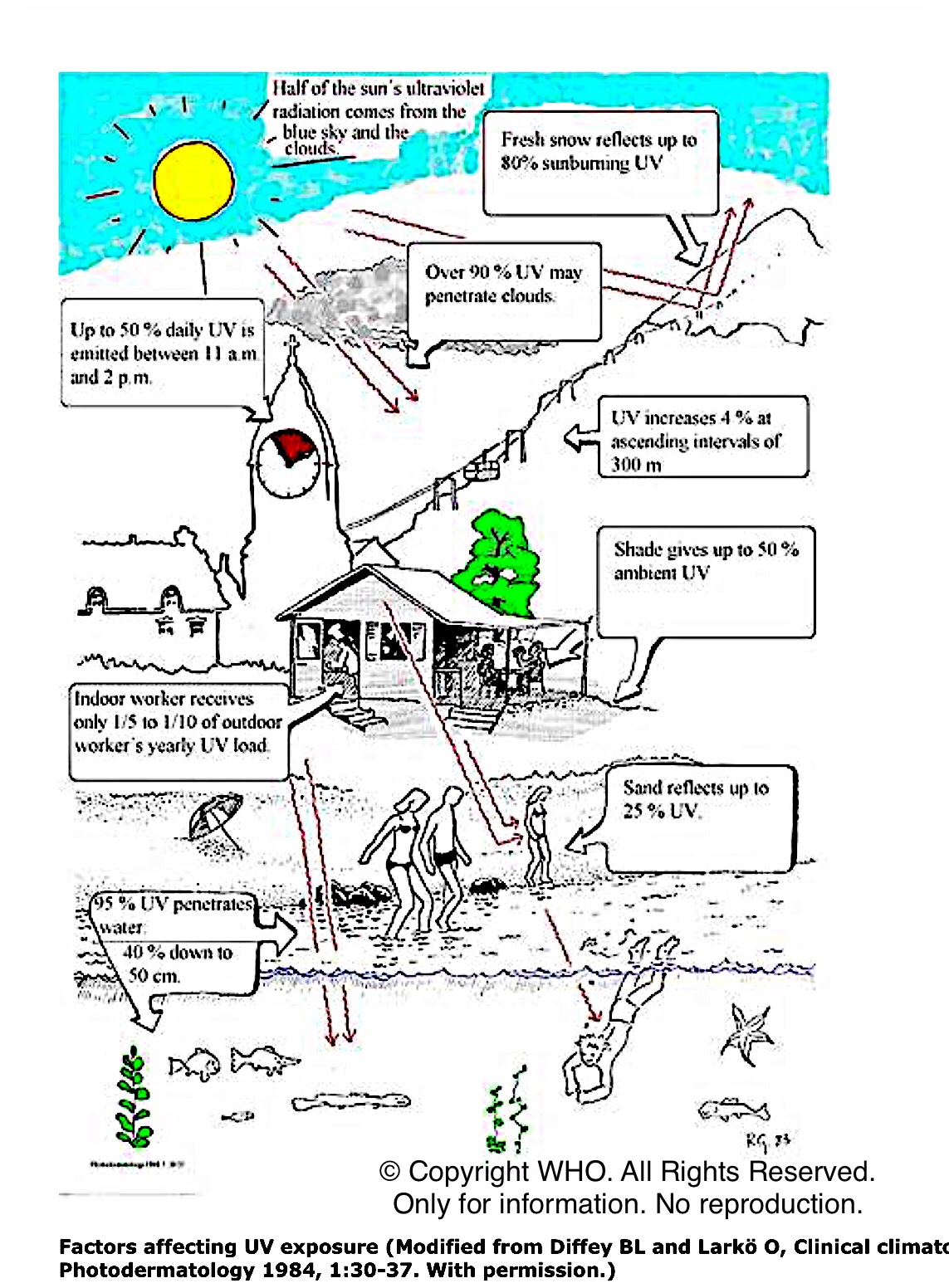
Vitamin D content is too low in foods (only in small quantities) to meet the adult body’s daily requirement (ca. 15-20 µg/600-800 IU), depending on age and for pregnancy. The food containing this small quantity are mushrooms, seafoods, green vegetables, eggs. Vitamin D (cholecalciferol / vitamin D3) is the only vitamin that the body produces itself, with the help of UVB (biologically damaging rays, most absorbed by the atmosphere, ozone) and sunlight. UV exposure is not a good idea, due to the harmful effects of UV rays. So please follow these recommendations for sun exposure:
1.avoid bright sunshine (e.g. 11:00 – 15:00)
2.protect your skin with a sunscreen
3.protect your eyes with sunglasses
In summer the body’s vitamin D production is usually sufficient. However, when there is a deficiency or an increased need, vitamin D can be taken in the form of drops, based on consultation with a physician.
The scientific sources of this text are:
the Swiss Cancer League (DE, FR, IT, EN) in Vitamin D
the World Health Organization (WHO) in http://www.who.int/uv/publications/proUVrad.pdf
For more (EN, FR, other languages) on http://www.who.int/uv/fr/
For more information, visit the Swiss Authorities link in different languages (DE, FR, IT). Please choose your language at the top of the website.
At the bottom of this website under “further information” , you can find 3 documents as pdf, explaining all about vitamin D (Q&A, scientific information, recommendations). I invite you to read them, the informations are up-to-dated and reliable (here the link of the document: DE, FR, IT: raccomandazioni-vitamina-d)

